SAP
Introduction:
SAP was founded in 1972 in Walldorf, Germany. It stands for Systems, Applications and Products in Data Processing. Over the years, it has grown and evolved to become the world premier provider of client/server business solutions for which it is so well known today. The SAP R/3 enterprise application suite for open client/server systems has established a new standards for providing business information management solutions.
SAP is collection of modules. Each module is collection of application. Each application is collection of screens. Each screen is related to table. Primary and foreign key relationship between the tables are called as RDBMS.
Features of SAP:
SAP designed based on RDBMS.
SAP can be customized using ABAP.
SAP highly integrated package.
SAP is database independent.
e.g. .NETàSQL server.
JAVAàJDBC
ABAPà JDBC
SQL server
DB2
MAXDB
SAP designed based on open systems (70% logic already given by sap).
SAP is available in 14 different languages.
SAP is international package.
SAP support all types of industry specific solutions.
SAP is highly versatile (OS independent). Runs on 6 different platforms (UNIX is best).
It is designed based on german language. Naming conventions are based on german language.
EKKOàEBELN.
2. IDES
Software’s in sap:
1. Production
It is for real time all the end users in real time have to work with this software.
Live data stored in production software.
2. IDES
It stands for International Demonstration & Educational system.
It is also known as training software. For end user training in real time.
In production software only live data is stored.
Where as in IDES dummy data is stored for training purpose.
SAP product are consider excellent but not perfect. The main problems with software product is that it can never be perfect.
The main advantage of using SAP as your company ERP system is that SAP have a very high level of integration among its individual applications which guarantee consistency of data throughout the system and the company itself.
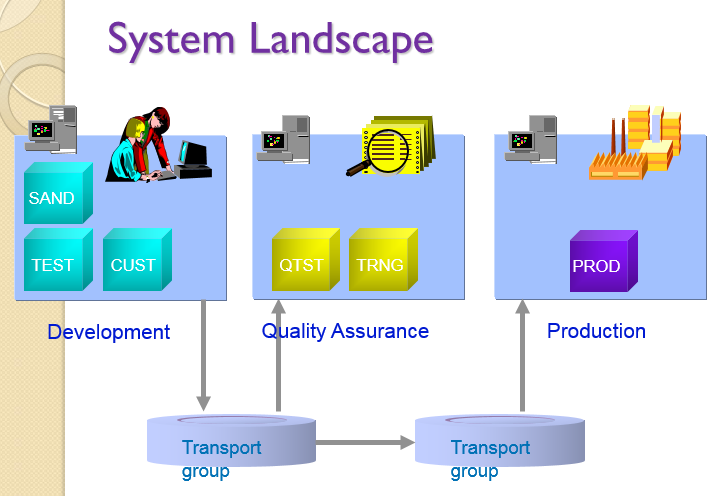
In a standard SAP project system, it is divided into three environments, Development, Quality Assurance and Production.
The development system is where most of the implementation work takes place. The quality assurance system is where all the final testing is conducted before moving the transports to the production environment. The production system is where all the daily business activities occur. It is also the client that all the end users use to perform their daily job functions. To all company, the production system should only contains transport that have passed all the tests.
SAP is a table drive customization software. It allows businesses to make rapid changes in their business requirements with a common set of programs. User-exits are provided for business to add in additional source code. Tools such as screen variants are provided to let you set fields attributes whether to hide, display and make them mandatory fields.
List of SAP Products:
This presents a partial list of products of the enterprise software company SAP AG.
1. SAP Customer Relationship Management (SAP CRM).
2. SAP Enterprise Resource Planning (SAP ERP).
3. SAP Product Lifecycle Management (SAP PLM).
4. SAP Supply Chain Management (SAP SCM).
5. SAP Supplier Relationship Management (SAP SRM).
1. SAP CRM (Customer Relationship Management)
SAP CRM supports all customer related processes and activities like sales and services. It enables the collaboration between the in-house employees, field employees, partners and customers. SAP CRM supports various types of interaction channels like internet, Mobile Phones etc. to communicate with customers directly.
2. SAP ERP (Enterprise Resource and Planning)
The application lets your people work more quickly and cost-effectively – connecting them directly to business processes and delivering the information and capabilities they need to make decisions and take action. It also enables you to innovate and adapt to the changing requirements of your industry – at lower cost and with greater speed.
SAP ERP- SEM (Strategic Enterprise Management Software): SAP Strategic Enterprise Management (SAP SEM) delivers end-to-end ERP software capabilities to support the entire performance management life cycle, including Consolidated Financial Reporting, Planning, budgeting & forecasting, corporate performance management and scorecards & Risk Management
SUB Modules:
SEM-BCS - Business Consolidation
SEM-BIC - Business Information Collection
BW-BPS - Business Planning and Simulation
SEM-CPM - Corporate Performance Monitor
SEM-SRM - Stakeholder Relationship Management
3. SAP Product Lifecycle Management (SAP PLM)
Product Lifecycle Management is a collection of solutions that can be used to digitally create and maintain product information to be made available to the entire organization at any point of time.
It provides all needed information about the complete product and asset life cycle through the extended supply chain, thereby ensuring legal compliance.
SUB Modules
SAP PLM_RM - Recipe Management
SAP PLM_AM - Audit Management
SAP PLM400 - Quality Management
SAP PLM410 - Quality Notifications
SAP PLM405 - Quality Inspections
SAP PLM425 - QM in Sales and Distribution
4. SAP SCM (SAP Supply Chain Management)
SAP Supply Chain Management (SAP SCM) enables collaboration, planning, execution, and coordination of the entire supply network, empowering you to adapt your supply chain processes to an ever-changing competitive environment.
SAP – APO - SAP Advance Planning and Optimization
SAP – OCH - SAP Inventory Collaboration Hub
SAP – EM - SAP Event Management
5. SAP SRM (Supply Relationship Management)
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) enables the full range of supply and procurement activities from the strategy stage to execution.
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) enables the full range of supply and procurement activities from the strategy stage to execution.
SAP Business Suite Definition:
SAP Business Suite is a collection of various SAP enterprise software that ensure optimized execution of business strategies. It consists of the ABOVE SAP Systems:
Business Solutions:
SAP Portal (EP)
SAP Exchange Infrastructure (XI) (From release 7.0 onwards, SAP XI has been renamed as SAP Process Integration (SAP PI))
SAP HANA (High-performance Analytics Appliance)
SAP Net Weaver Application Server (Web AS)
TECHNICAL MODULES:
SAP ABAP module – Advanced Business Application Programming.
SAP Basis module – Basis Admin, administration of SAP.
SAP BI module – Business Intelligence.
SAP BPC module – Business Planning and Consolidation.
SAP BODI module – Business Objects Data Integrator.
SAP EP module -Enterprise Portal.
SAP GRC module – Group Risk Compliance. If you are interested in earning your certification of completion for a training course in SAP GRC, take a look at this class. In this training course you will gain valuable insights into risk, compliance, and control management for an enterprise by studying GRC RAR.
SAP MDM module – Master Data Management.
SAP Net weaver module – The technical foundation for SAP applications. Some may find that SAP Net weaver is a bit tricky to get the hang of at first. If this is true for you, try taking a course on SAP Net weaver training and learn from an instructor with industry experience.
SAP Security module – Security for enterprise operations.
SAP Solution Manager Module – Manages technical support for distributed systems.
SAP XI module – Allows the implementation of cross-system processes on services.
SAP PI module – Enterprise application integration (EAI) software.
FUNCTIONAL MODULES:
SAP APO module – Advanced Planner Optimizer.
SAP CO module – Controlling.
SAP CRM module – Customer Relationship Management.
SAP CS module – Customer Service.
SAP EC module – Enterprise Controlling.
SAP EHS module – Environment, Health & Safety.
SAP EWM module – Extended Warehouse Management.
SAP FI module – Financial Accounting.
SAP FM module – Fleet Management.
SAP FSCM module -Financial Supply Chain Management.
SAP HR module – Human Resources.
SAP IM module – Investment Management.
SAP MM module – Materials Management.
SAP PLM module – Product Lifecycle Management.
SAP PM Module – Plant Maintenance.
SAP PP module – Production Planning.
SAP PS module – Project Systems.
SAP QM module – Quality Management.
SAP RE module – Real Estate.
SAP SCM module – Supply Chain Management.
SAP SD module – Sales and Distribution. SAP SD is one of the most popular SAP modules.
SAP SEM module – Strategic Enterprise Management.
SAP SM module – Service Management.
SAP TR module – Treasury.
SAP WM module – Warehouse Management.
SAP LO module – Logistics General.
INDUSTRY SPECIFIC MODULES (KNOWN AS SAP IS):
SAP IS Aerospace & Defense – Air and military industries.
SAP IS Automotive – Automobile manufacturing industries.
SAP IS Banking – Financial Industries, Banking, and Market Risk Management.
SAP IS Chemicals – Chemical industries.
SAP IS Consumer Products – Consumer product industries.
SAP IS Defense & Security – Defense and security industries.
SAP IS Engineering, Construction, and Operations – Construction and engineering Companies.
SAP IS Healthcare – Hospitals and healthcare institutions.
SAP IS Higher Education & Research – Campus management.
SAP IS High Tech – High tech industries.
SAP IS Industrial Machinery and Components – Heavy machinery manufacturing companies.
SAP IS Insurance – Insurance companies and Currency Markets.
SAP IS Life Sciences – Life sciences industry.
SAP IS Media – Communication and Publishing industries.
SAP IS Mill Products – Mill product industries.
SAP IS Mining – Mining industries.
SAP IS Oil & Gas – Oil and Gas Industries.
SAP IS Professional Services – Professional services industry.
SAP IS Pharma – Pharmaceutical industries.
SAP IS Public Sector – Public Sector and Administration.
SAP IS Retail – Supermarkets and Retail industry.
SAP IS Telecommunications – Telecommunication operators.
SAP IS Transportation & Logistics – Transportation and logistics industry.
SAP IS Utilities – Utility industries.
SAP IS Wholesale Distribution – Wholesale distribution industry.
Briefly Functional Modules
SAP FI - Financial Accounting:
Designed for automated management and external reporting of General Ledger (GL), Accounts Receivable (AR), Accounts Payable (AP), and Asset Management (AM) with a user-defined chart of accounts.
External reporting, such as income statement and balance sheet Represents cost and revenue flows throughout the organization
Aids in organizational decision making
Supports internal reporting such as cost center reports.
SUB Modules
SAP FI-GL - General Ledger
SAP FI-AP - Accounts Payable
SAP FI-AR - Account Receivable
SAP FI-SL- Special Purpose Ledger
SAP FI-BL – Bank Accounting
SAP AA - Asset Accounting: AA provides tools to acquire, depreciate, evaluate, and retire assets. The kinds of assets covered are fixed, low value, leased, and real estate.
Low value assets depreciate in the year they are bought and are often aggregated as a single asset master record.
Depreciation often needs to be tracked (for more than one reason), so SAP R/3allows you to depreciate the same piece of equipment in several parallel ways.
SAP CO – Controlling: SAP CO Module helps management by providing reports on cost centers, profit centers, contribution margins, profitability, etc. They also deal with cost accounting processing, analytical reporting, and audit-controlling spectrums.
SUB Modules
SAP CO-CEA - Cost Element Accounting
SAP CO-CCA - Cost Center Accounting
SAP CO- Internal Orders
SAP CO- Activity-Based Costing
SAP CO-PC- Product Cost Controlling
SAP CO-PA- Profitability Analysis
SAP CO-PCA- Profit Center Accounting
SAP CO-OM- Overhead Cost controlling
SAP CO-ML- Material Ledger
SAP TR – Treasury:
SUB Modules
SAP TR-CB - Cash Budget Management
SAP TR-MRM - Market Risk Management
SAP TR-CM - Cash Management
SAP TR-LO - Loans Management
SAP TR-TM - Treasury Management
SAP TR-FM - Funds Management
SAP IM - capital Investment Management: It used for planning, budgeting and monitoring of a comprehensive budget .An investment program represents the planned or budgeted costs for the capital investments of an enterprise. Using investment programs, you can obtain an overview of planning and budgeting processes in complex enterprise structures for all investments and large projects of the group, while at the same time maintaining strict budgetary control.
Human resource management:
SAP HCM (Human Capital Management) Or SAP HR - Human Resource:: Takes care of payroll, time recording, applicant administration, and organization data. It supports the planning and control of personnel activities. It consists of all master data, system configuration, and transactions to complete the Hire to Retire (or, as some say, Fire) process.
SUB Modules
Organizational Management (OM)
Personnel Administration (PA)
SAP PA - Personnel Administration
SAP PA-APP - Applicant Management
SAP PA-BEN - Benefits
SAP PA-EMP - Employee Management
SAP PA-INW - Incentive wages
SAP PA-PAY - Payroll
SAP PA-TIM - Time Management
SAP PA-TRV - Travel Expenses
Personnel planning and Development(PD)
SAP PD-OM - Organizational Management
SAP PD-RPL - Room Reservations Planning
SAP PD-WFP - Workforce Planning
SAP PD-SCM - Seminar and Convention Management
SAP PD-PD - Personnel development
Recruitment
Time Management (TM)
Travel Management (TM )
Payroll
Benefits
Compensation Management
Personal cost Planning
Budget Management
Training and Event Management
Logistic and Manufacturing - Mainly SD/MM:
SAP SD - Sales & Distribution: This module includes the business processes used to sell and deliver products and services to customers and business partners. Information about the product and customers (both of which are stored in the master data) is used in SD.
SUB Modules
SAP SD-MD - Master Data
SAP SD-CAS - Sales Support
SAP SD-SLS - Sales
SAP SD-SHP - Shipping
SAP SD-TR - Transportation
SAP SD-BIL - Billing
SAP SD-SIS - Sales Information System
SAP SD-EDI - Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
SAP SD-GF General Sales Functions
SAP LE - Logistic Execution
SAP MM - Material Management: The grouping of management functions supporting the complete cycle of material flow, from the purchase and internal control of production materials to the planning and control of work in process to the warehousing, shipping, and distribution of the finished product.
SUB Modules
SAP MM-PUR - Purchasing
SAP MM-IM - Inventory Management
SAP MM-WM - Warehouse Management
SAP MM-IV - Invoice Verification
SAP MM-IS - Information System
SAP MM-CBP - Consumption Based Planning
SAP MM-EDI - Electronic Data Interchange
SAP MRP - Materials Requirement Planning
SAP ML - Material Ledger.
SAP PP - Production Planning:This module supports functions for the overall level of manufacturing output and other activities to best satisfy the current planned levels of sales (sales plan or forecasts), while meeting general business objectives of profitability, competitive customer lead times as expressed in the overall business plan. One of its primary purposes is to establish production rates that will achieve management’s objective of satisfying customer demand, by maintaining, raising or lowering inventories or backlogs, while usually attempting to keep the workforce relatively stable.
Sub Modules
SAP PP-SOP - Sales and Operations Planning
SAP PP-CRP - Capacity Requirement Planning
SAP PP-MP - Master planning
SAP PP-ATO - Assembly orders
SAP PP-BD - Basic Data
SAP PP-IS - Information System
SAP PP-KAB - Kanban/Just-in-Time
SAP PP-MRP - Material Requirements Planning
SAP PP-PDC - Plant Data Collection
SAP PP-PI - Production Planning for Process Industries
SAP PP-REM - Repetitive Manufacturing
SAP PP-SFC - Production orders
SAP DS - Detailed Scheduling.
SAP PM - Plant Maintenance: Supports the planning, processing, and completion of plant maintenance tasks. Allows for planners to schedule routine maintenance in a way that is least disruptive for manufacturing and sales requirement.
SUB Modules
SAP PM-EQM - Equipment and Technical Objects
SAP PM-IS - PM Information System
SAP PM-PRM - Preventive Maintenance
SAP PM-PRO - Maintenance Projects
SAP PM-SM - Service Management
SAP PM-WOC - Maintenance Orders Management.
SAP QM - Quality Management: Supports the quality inspection aspects of the business, including purchasing, research, and sales. Allows for buyers and manufacturing personnel to track inspection lots and test results.
SUB Modules
SAP QM-QP - Quality Planning
SAP QM-IM - Quality Inspection processing
SAP QM-QC-AQC - Quality control
SAP QM-IT - Test equipment management
SAP QM-QN - Quality notifications
SAP QM-CA - Quality certificates
SAP QM-CR - General functions
SAP QM-PT-RP - Control in logistics
SAP PS - Project System: Helps you to plan, manage, control, and figure the cost of R&D projects, and soon. The common tasks revolve around allocation of people, resources, and money within the framework of schedule and task relationships.
SUB Modules
SAP PS-CAF - Payments
SAP PS-CON - Confirmation
SAP PS-COS - Costs
SAP PS-CRP - Resources
SAP PS-DAT - Dates
SAP PS-DOC - Documents
SAP PS-IS - Information System
SAP PS-MAT - Material
SAP PS-PRG - Progress
SAP PS-REV - Revenues and Earnings
SAP PS-SIM - Simulation
SAP PS-ST - Structures
SAP PS-VER - Versions
SAP LO - General Logistics:
SUB Modules
SAP LO-AB-TC - Trading Contract
SAP LO-BM - Batches
SAP LO-ECH - Engineering Change Management
SAP LO-EHS - Environment Management
SAP LO-EWB - Engineering Workbench
SAP LO-HU - Handling Unit Management
SAP LO-LIS - Logistics Information System
SAP LO-MAP - Merchandise & Assortment Planning
SAP LO-MD - Logistics Basic Data
SAP LO-MDS - Merchandise Distribution
SAP LO-PDM - Product Data Management
SAP LO-PR - Forecast
SAP LO-RIS - Retail Information System
SAP LO-SCI - Supply Chain Planning Interface
SAP LO-SRS - Retail Store
SAP LO-VC - Variant Configuration
SAP LO170 - Quality Management
SAP LO705 - Quality Inspections
SAP LO710 - Quality Notifications
SAP LO725 - Quality Certificates
SAP LE - Logistic Execution
Cross Application Module
Cross Application (X-Apps)
SAP MII for Manufacturing Integration & Intelligence
SAP APO - Advanced Planner and Optimizer
SAP Live Cache
SAP WF – Workflow: Links the integrated SAP R/3 application modules with cross-application technologies, tools, and services, including e-mail.
Workflow allows you to set up the followings:
Maintain your company’s organization structure according to responsibility.
Link the predefined standard tasks with the authorized agents in your company.
Activate existing event receiver links between triggering events and consuming workflow tasks.
Name a technical person responsible for each standard workflow template.
SAP GRC -Governance, Risk, and Compliance
SAP SDN - SAP Developer Network
SAP Virsa
SAP GTS - Global Trade Services
SAP EM - SAP Emissions Management
SAP CPM - Corporate Performance Management
SAP SEM - Strategic Enterprise Management
SAP BPS Business Planning and Simulation.
SAP SM Strategy Management - Service Management (SM) module is fully capable to support customer demands more effectively. It has got an excellent reporting functionality, which helps the management by providing the reports, which would help them, identify areas of improvement.
SAP PS- Project systems:
Project System provides tools to track project milestone, costs and resources. SAP's Project System module contains tight integration to the Controlling, Human Resources, and Logistics modules. It utilizes personnel records from HR, rolls costs into Controlling and links to materials or customers in the Logistics modules.
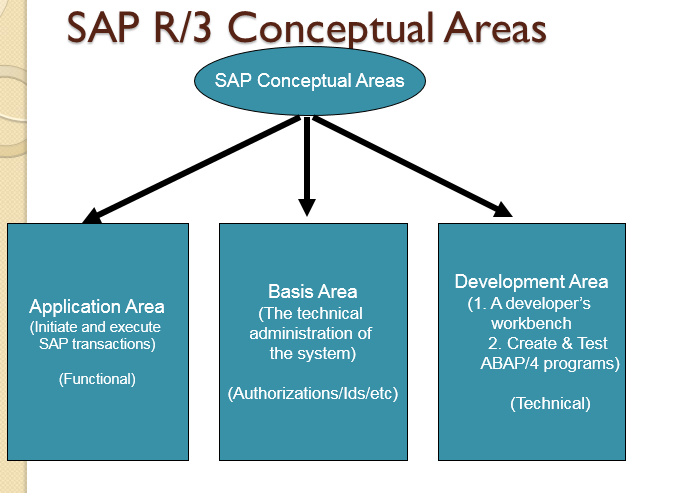
SAP IS - Industry Solutions:
Basic consultants:
Installation (SAP R/3, Solution management, Net weaver, Component)
Administration (Client Admin, User Admin, Backups)
Configuration (Printer, STMS, RFC)
Maintainance (server maintainance, System Performance, Back ground jobs)
Functional consultants:
Handles data in applications.
Data customization.
Getting requirement from end user.
Preparing user manuals.
End user training.
Preparing functional documents.
Abap consultants:
Not software engineer.
Preparing technical document.
Creating objects from scratch (Implementation project)
Modifying existing objects (support projects)
Testing:
EnduseràFunctional consultantàTechnical consultant.
1. What is a client in SAP terminology?
S/W component that uses the service (offered by a s/w component) is called a Client. At the same time these clients may also be servers for other services.
2. What is a SAP system?
The union of all s/w components that are assigned to the same databases is called as a SAP system.
3. What is the means of communications between R/3 and external applications?
The means of communication between R/2,R/3 and external applications is via the CPI-C handler or SAP Gateway, using the CPI-C Protocol.
4. What is the protocol used by SAP Gateway process?
The SAP Gateway process communicates with the clients based on the TCP/IP Protocol.
5. Expand CPI-C.
Common Program Interface Communication.
6. What is a Spool request?
Spool requests are generated during dialog or background processing and placed in the spool database with information about the printer and print format. The actual data is places in the Tem Se (Temporary Sequential objects).
7. What are different types of Log records?
S/W component that uses the service (offered by a s/w component) is called a Client. At the same time these clients may also be servers for other services.
2. What is a SAP system?
The union of all s/w components that are assigned to the same databases is called as a SAP system.
3. What is the means of communications between R/3 and external applications?
The means of communication between R/2,R/3 and external applications is via the CPI-C handler or SAP Gateway, using the CPI-C Protocol.
4. What is the protocol used by SAP Gateway process?
The SAP Gateway process communicates with the clients based on the TCP/IP Protocol.
5. Expand CPI-C.
Common Program Interface Communication.
6. What is a Spool request?
Spool requests are generated during dialog or background processing and placed in the spool database with information about the printer and print format. The actual data is places in the Tem Se (Temporary Sequential objects).
7. What are different types of Log records?
V1 and V2. V1 must be processed before V2. But, we can have more than one V2 logs.
8. What are the types of Update requests?
An update request can be divided into one primary (V1) and several Secondary update components (V2). Time-critical operations are placed in V1 component and those whose timing is less critical are placed in V2 components. If a V1 update fails, V2 components will not be processed.
9. Dialog work processes perform only one dialog step and then available for the next request.
10. Explain what is a transaction in SAP terminology.
In SAP terminology, a transaction is series of logically connected dialog steps.
8. What are the types of Update requests?
An update request can be divided into one primary (V1) and several Secondary update components (V2). Time-critical operations are placed in V1 component and those whose timing is less critical are placed in V2 components. If a V1 update fails, V2 components will not be processed.
9. Dialog work processes perform only one dialog step and then available for the next request.
10. Explain what is a transaction in SAP terminology.
In SAP terminology, a transaction is series of logically connected dialog steps.
11. Define service (within R/3)?
A service is a process or group of processes that perform a specific system function and often provide an application-programming interface for other processes to call.
12. What are the roll and page areas?
Roll and page areas are SAP R/3 buffers used to store user contexts (process requests). The SAP dispatcher assigns process requests to work processes as they are queued in the roll and page areas.
Paging area holds data from the application programs.
Roll area holds data from previous dialog steps and data that characterize the user.
13. What are the different layers in R/3 system?
Presentation Layer.
Application Layer.
Database Layer.
14. What are the phases of background processing?
Job Scheduling.
Job Processing.
Job Overview.
15. What components of the R/e system initiate the start of background jobs at the specified time?
The batch scheduler initiates the start of background job. The dispatcher then sends this request to an available background work process for processing.
16. Define Instance.
An instance is an administrative unit in which components of an R/3 systems providing one or more services are grouped together.
16. Define Instance.
An instance is an administrative unit in which components of an R/3 systems providing one or more services are grouped together.
The services offered by an instance are started and stopped at random. All components are parametrized using a joint instance profile.
A central R/3 system consists of a single instance in which all-necessary SAP services are offered. Each instance uses separate buffer areas.
17. From hardware perspective, every information system can be divided into three task areas Presentation, Application Logic and Data Storage.
The R/3 Basis software is highly suitable for use in multi-level client/server architectures.
18. What are R/3 Basis configurations?: A central system with centrally installed presentation software.
17. From hardware perspective, every information system can be divided into three task areas Presentation, Application Logic and Data Storage.
The R/3 Basis software is highly suitable for use in multi-level client/server architectures.
18. What are R/3 Basis configurations?: A central system with centrally installed presentation software.
Two-level client/server system with rolled out presentation software.
Two-level client/server system. Presentation and Application run on the same computer.
Three-level client/server system. Presentation, Application and database each run on separate computers.
19. What is a Service in SAP terminology?
A service refers to something offered by a s/w component.
10. What is Server in SAP terminology?
A component can consist of one process or a group and is then called the server for the respective service
What is SAP ABAP?
ABAP = Advanced Business Application Programming language It is an interpreted programming language that runs in the SAP ABAP Runtime environment. ABAP is the main language used for building solid-state business application solutions in the SAP Runtime environment. It has evolved over the years to include Object Oriented language extensions as well. |